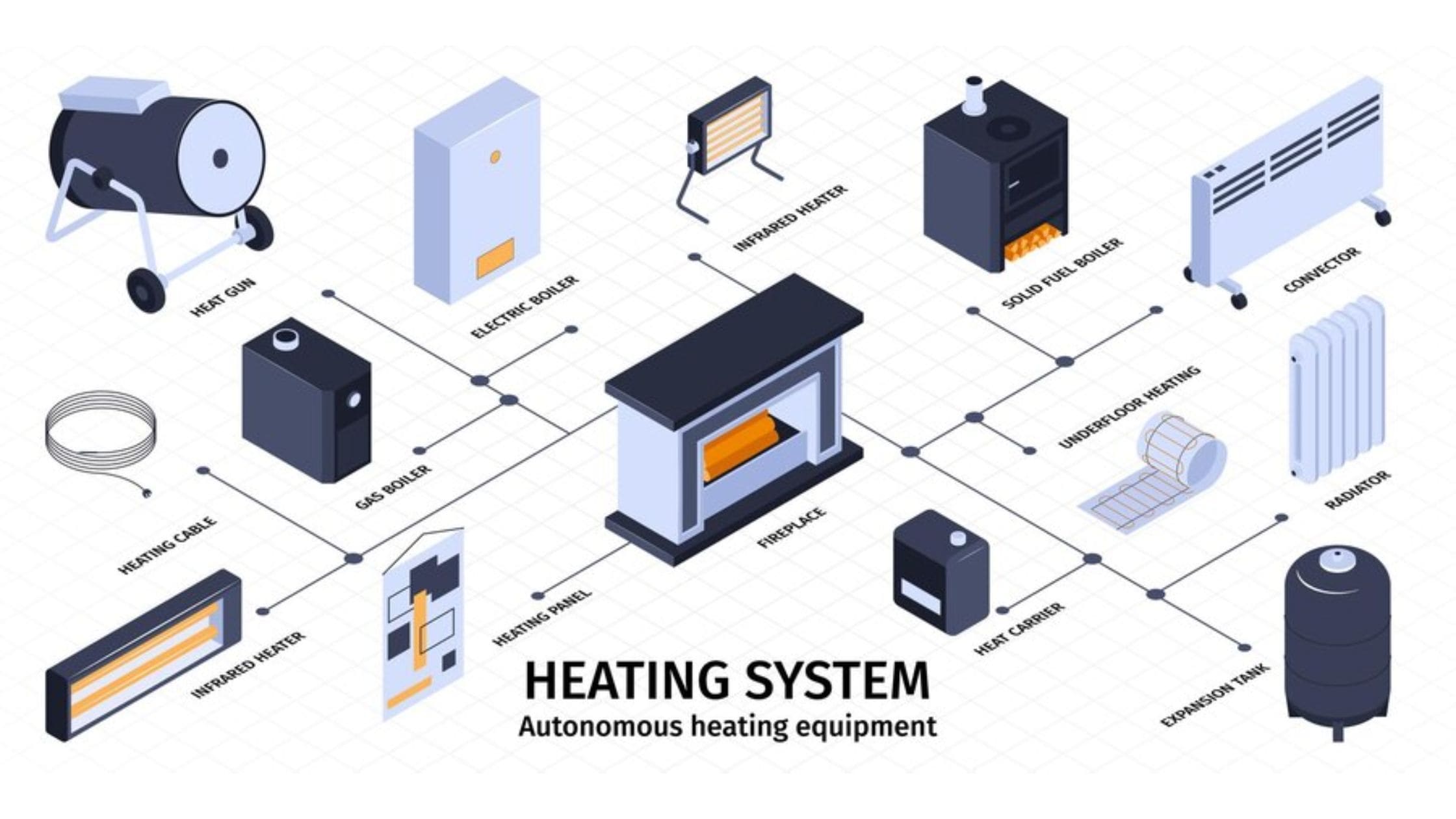
A proper heating system should provide comfort, energy efficiency, and low cost for residential and commercial buildings. House owners try to choose among various options of heating systems—central or zonal—to understand how a system works, its advantages, and types of heating systems. This thorough examination can help you select the best heating system for your house and space requirements, from traditional furnaces to energy-efficient heat pumps to radiant floor heating.
Central Heating System
The central heating system gives heat to the whole building from one source through ducts, pipes, or radiators. Large space heating systems prove very efficient while maintaining consistent temperatures throughout, with the frequent ability for customized thermostat control.
Furnaces (Forced Air Systems)

- How It Works: Furnaces heat the air using gas, electricity, or oil and then circulate it through ducts to different rooms using a fan and vents.
- Pros: Serves to heat a space quickly and efficiently allows indoor air filtering and humidification for better quality.
- Cons: It can lead to ‘hot spots’ in some places. It could also be the culprit behind dry air; its filters and ducts require periodic cleaning/maintenance.
Boilers (Radiant Heating Systems)
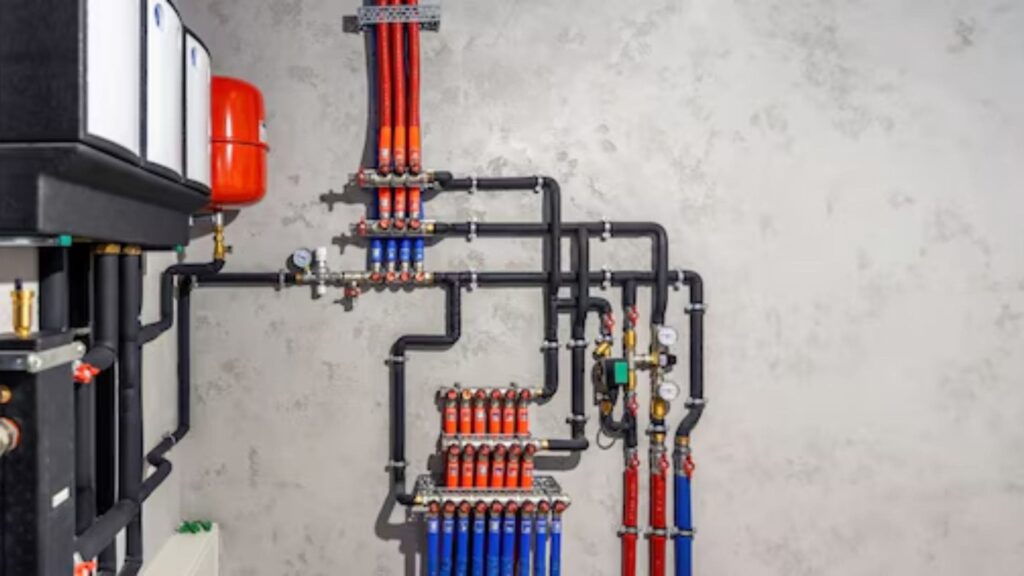

- How It Works: Boilers heat water that circulates via pipes to radiators or underfloor systems, providing warmth directly into rooms.
- Pros: It provides constant, comfortable heat without circulating air, which minimizes dust and allergens, making it perfect for allergic people.
- Cons: Generally costlier to set up, and temperature changes are made reasonably slowly compared to the forced-air systems. Sometimes, it takes space for the boiler unit.
Heat Pumps
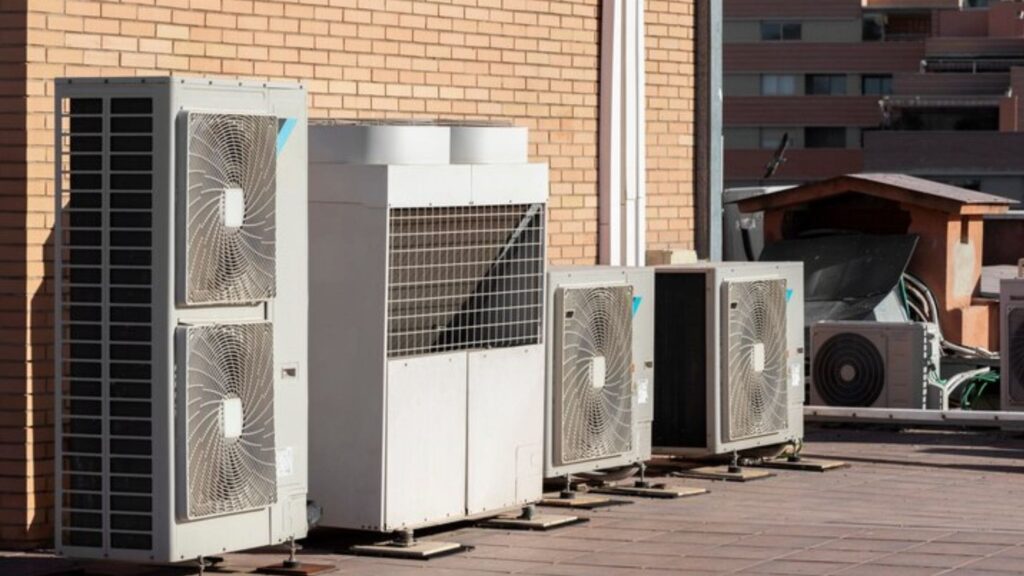

- How It Works: Heat pumps transfer heat energy from the outside air or soil to indoor spaces. They all work on electricity and are reversible to cool indoor spaces during warmer months.
- Pros: It is extraordinarily efficient and provides heating and cooling options, which can save utility costs and reduce one’s carbon footprint.
- Cons: It is costly to install, its efficiency drops off in frigid climates, and it usually needs a backup heating source to work well.
Hybrid Heating System
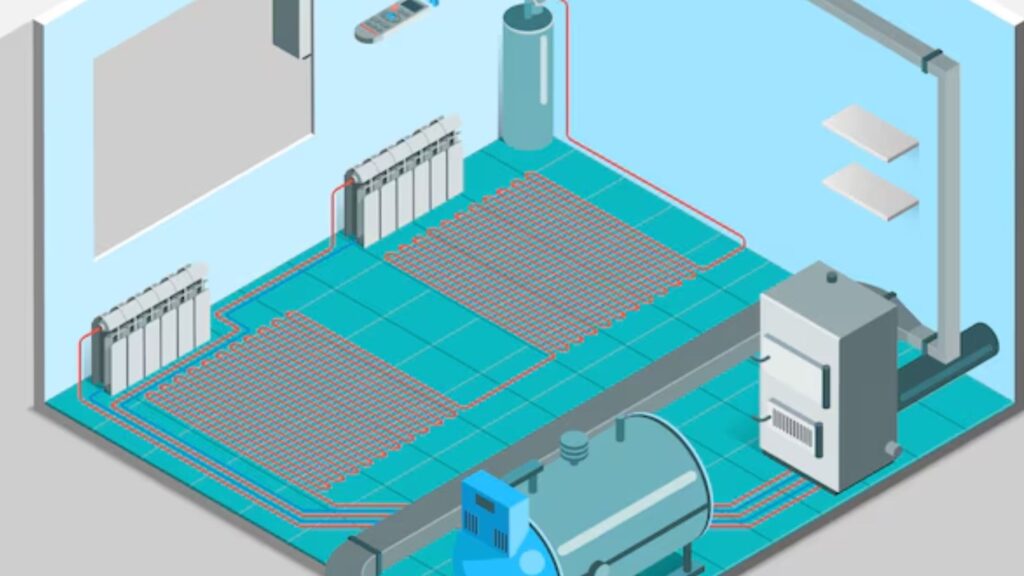
- How It Works: Hybrid heating systems team a heat pump with a traditional furnace, automatically switching between the two depending on outside air temperatures to maintain optimum energy efficiency.
- Pros: It is flexible and efficient because, in mild climatic conditions, it uses a heat pump, while when it gets colder, the furnace takes over, saving heating costs.
- Cons: Higher initial costs and increased servicing due to integrating two systems.
Zonal Heating Systems
The heating from zonal heating systems is well concentrated, in that it can provide better controls and efficiencies in a particular area or room. Unfortunately, these systems are suited for use in small areas or as further assistance to central heating systems.
Electric Resistance Heating
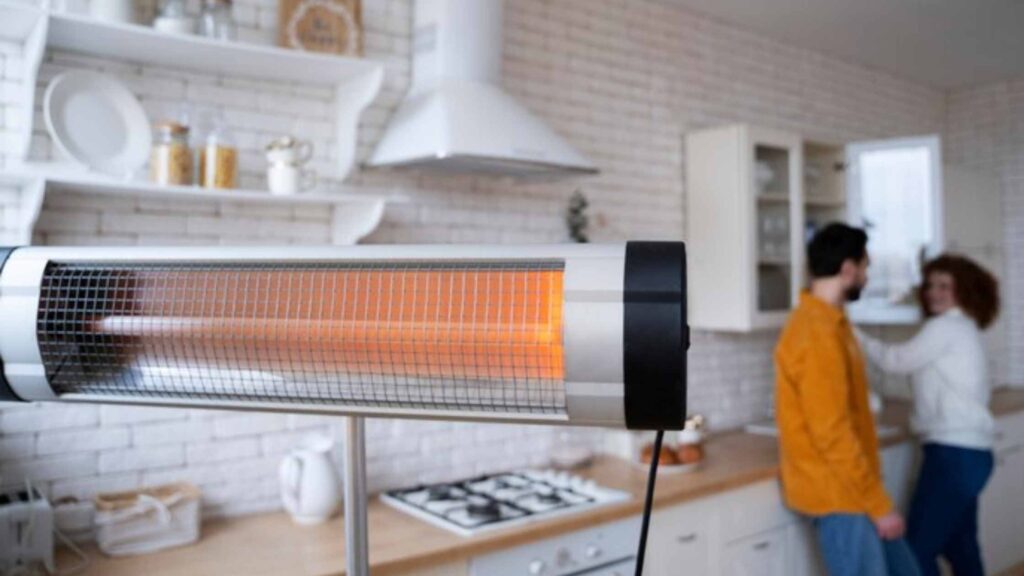

- How It Works: This heating works by direct electrical energy converted to heat. Baseboards, wall heaters, or space heaters warm specific rooms or zones.
- Pros: These heaters are easily installable and practical for quick, localized heating in relatively small areas while offering top-notch temperature control.
- Cons: They are often expensive to operate due to their high electrical usage, making them less cost-effective for larger areas and/or over more extended periods in cold climates.
Radiant Floor Heating
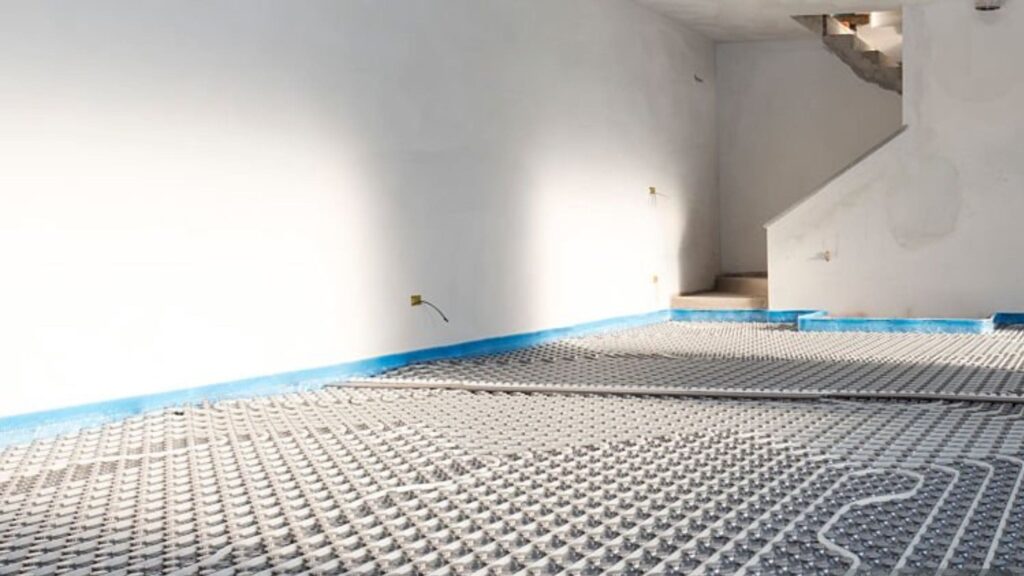

- How it works: Radiant floor heating is provided by electric coils or heated water tubes beneath the floor that radiate upward, thus warming the room uniformly.
- Pro: It supplies comfortable, even heat without circulating air, which reduces allergens and makes for a warm floor surface, ideal for cold climates.
- Cons: It is a costly installation that takes time, especially in existing ones; it could also take a long time compared to forced-air systems to heat a room.
Ductless Mini-Split Systems
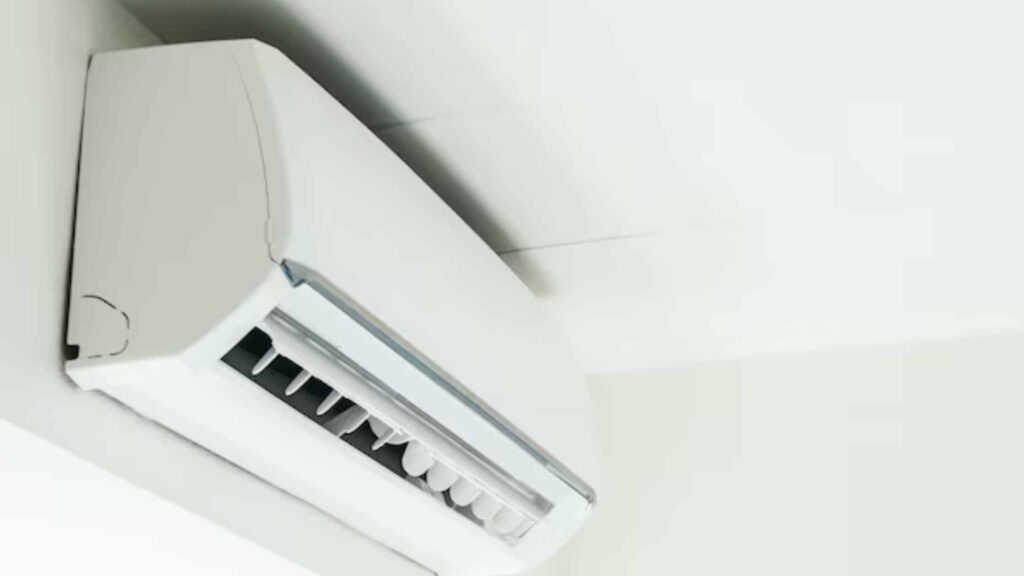

- How it works: Ductless mini-split systems combine an outdoor compressor with indoor air-handling units to provide heating or cooling directly to distinct zones without ducts.
- Pros: It is energy-efficient and allows for excellent room temperature regulation, saving wasted energy and reducing utility bills.
- Cons: Higher upfront costs for installation are required, the wall-mounted units are unsightly, and they may not match every interior theme.
Wood-burning or Pellet Stoves
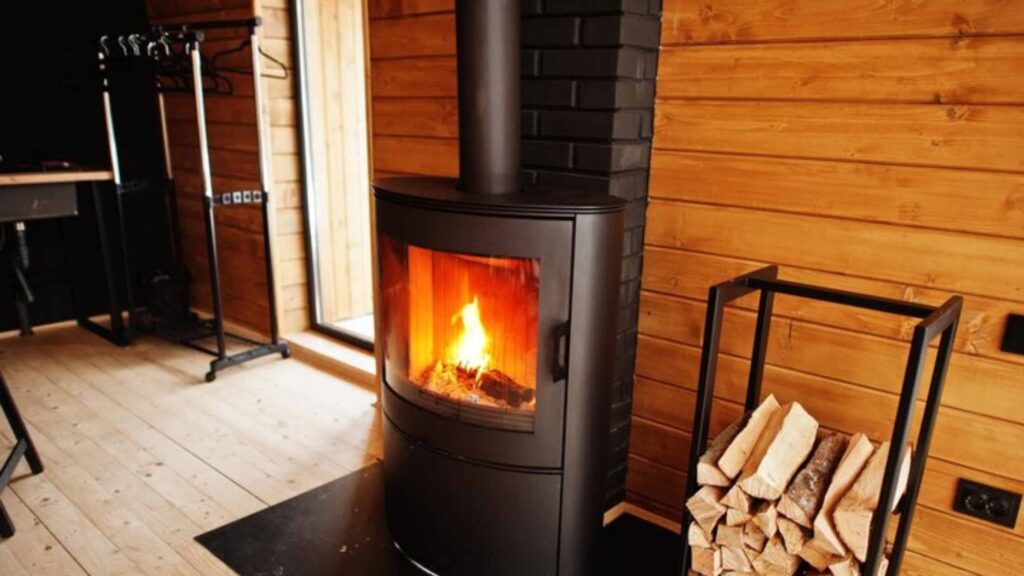

- How it Works: Woodburning or pellet stoves generate heat by burning wood logs or compressed pellets. The heat is then radiated directly into the room, sometimes connected with a chimney for ventilation.
- Pros: Offers cozy, rustic ambiance and can be more heating-economical for small areas, particularly in an off-grid/rural setting.
- Cons: The cons are that they require frequent refueling and cleaning and produce smoke or odors; good ventilation is necessary, or indoor air emissions could suffer.
How to Choose the Best Heating System Space
The best heating system is chosen according to space, budget, and climate needs. This section provides residential and commercial settings with the best heating solutions, enabling one to make an informed, energy-efficient, and cost-effective choice in heater selection.
Residential Space
The needs of your space, budget, and climate determine your best choice of heating system. The following section highlights optimal heating options for residential and commercial applications to ensure that one can make a justified, energy-efficient, and cost-effective choice. A heat pump or hybrid heating system is usually best for residential spaces due to its energy efficiency, dual heating and cooling capability, and lower operational cost.
Commercial Space
Coupled with this is a central heating system, usually consisting of a furnace or boiler. These systems are ideally installed for larger areas, as they can distribute even and consistent heat to several rooms or even floors. Central systems can be installed with thermostats to offer a zoned control that further assists in optimizing energy use and maintaining comfortable temperatures in busy work environments.
For the past decade, All About Air Conditioning & Heating LLC has provided San Antonio with reliable HVAC installation, repair, and maintenance, ensuring maximum comfort and efficiency for all residential and commercial clients.